Association of Glycolysis-Enhancing α-1 Blockers With Risk of Developing Parkinson Disease
Abstract
Importance: Parkinson disease (PD) is a common neurodegenerative disease. A treatment that prevents or delays development of PD is a critical unmet need. Terazosin and closely related drugs were recently discovered to enhance glycolysis and reduce PD progression in animal models and human clinical databases.
Objective: To determine whether use of terazosin, doxazosin, and alfuzosin is associated with a decreased risk of developing PD.
Design, Setting, and Participants: This cohort study used active comparator control and propensity score-matched data from Danish nationwide health registries, including the Danish National Prescription Registry, the Danish National Patient Registry, and the Danish Civil Registration System, from January 1996 to December 2017 and data from the Truven Health Analytics MarketScan database from January 2001 to December 2017. Men without PD who newly initiated terazosin/doxazosin/alfuzosin therapy or tamsulosin therapy, which is used for a similar indication (benign prostatic hyperplasia or unspecified urinary problems) but does not enhance glycolysis, and had at least 1 year of follow-up after medication start were included. In Denmark, the database included all residents, while the Truven database is a compilation of insurance claims across the US. Data were analyzed from February 2019 to July 2020.
Exposures: Patients who used terazosin/doxazosin/alfuzosin vs tamsulosin. Additional dose-response analyses were carried out.
Main Outcomes and Measures: Differences in the hazard of developing PD identified by diagnoses or use of PD-specific medications between patients who ever used terazosin/doxazosin/alfuzosin or tamsulosin.
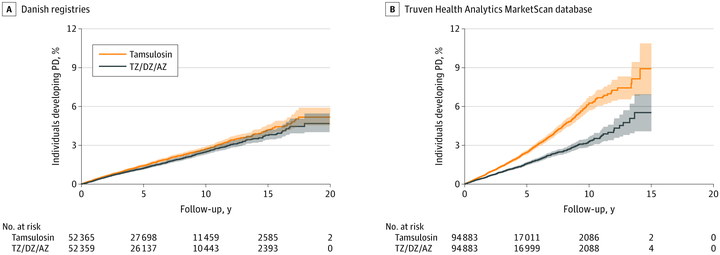
Results: A cohort of 52 365 propensity score-matched pairs of terazosin/doxazosin/alfuzosin and tamsulosin users were identified in the Danish registries, of which all were male and the mean (SD) age was 67.9 (10.4) years, and 94 883 propensity score-matched pairs were identified in the Truven database, of which all were male and the mean (SD) age was 63.8 (11.1) years. Patients in the Danish cohort who used terazosin/doxazosin/alfuzosin had a hazard ratio (HR) for developing PD of 0.88 (95% CI, 0.81-0.98), and patients in the Truven cohort had an HR of 0.63 (95% CI, 0.58-0.69). There was a dose-response association with short-duration, medium-duration, and long-duration use of terazosin/doxazosin/alfuzosin users having a decreasing HR in both the Danish cohort (short: HR, 0.95; 95% CI, 0.84-1.07; medium: HR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.77-1.01; long: HR, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.66-0.95) and Truven cohort (short: HR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.64-0.76; medium: HR, 0.58; 95% CI, 0.52-0.64; long: HR, 0.46; 95% CI, 0.36-0.57).
Conclusions and Relevance: These data suggest that users of terazosin/doxazosin/alfuzosin are at lower hazard of developing PD compared with users of tamsulosin. Future work is needed to further assess this association.